Enough of that Foundations garbage. That was only 5% of the test! You could literally not know any of that and still get a 5. So, let's put on our 'big-boy-pants" and start covering some real history. This is where it all begins. Yeah, in Foundations you have things like... Humans, Fire, Tools, Hierarchy, Religion, Writing. But, this is where history actually takes form. This is where you will get your stereotypical views of certain areas. This is where Western Europe takes root. This is where India becomes India. This is where China becomes China. Later on, areas like Africa, the Middle East, the Americas, et al will come into their own. This era really deals with the Classical Civilizations (Mediterranean, India, China) and the trade between them and what goes along with that.
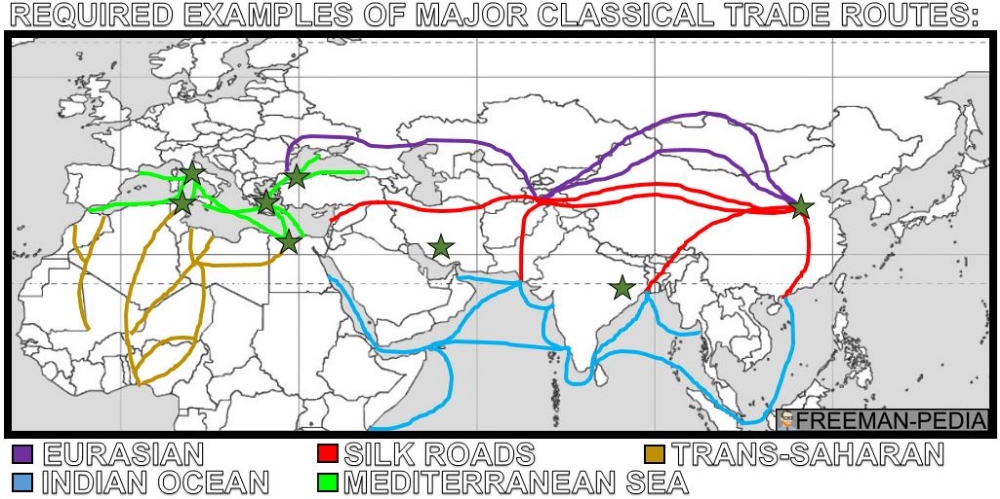
The above map was created using the geographic references from this era in the AP World History curriculum. Every geographic reference for this unit appears on this map.
As states and empires increased in size and contacts between regions multiplied, religious and cultural systems were transformed. Religions and belief systems provided a bond among the people and an ethical code to live by. These shared beliefs also influenced and reinforced political, economic, and occupational stratification. Religious and political authority often merged as rulers (some of whom were considered divine) used religion, along with military and legal structures, to justify their rule and ensure its continuation. Religions and belief systems could also generate conflict, partly because beliefs and practices varied greatly within and among societies.
I. Codifications and further developments of existing religious traditions provided a bond among the people and an ethical code to live by.
II. New belief systems and cultural traditions emerged and spread, often asserting universal truths.
III. Belief systems generally reinforced existing social structures while also offering new roles and status to some men and women.
A. Confucianism emphasized Filial Piety.
B. Some Buddhists and Christians practiced a Monastic Life.
IV. Other religious and cultural traditions continued and in some places incorporated into major religious traditions.
A. Shamanism, animism, and ancestor veneration continued in their traditional forms in some instances, and in others were incorporated into other religious traditions.
As the early states and empires grew in number, size, and population, they frequently competed for resources and came into conflict with one another. In quest of land, wealth, and security, some empires expanded dramatically. In doing so, they built powerful military machines and administrative institutions that were capable of organizing human activities over long distances, and they created new groups of military and political elites to manage their affairs. As these empires expanded their boundaries, they also faced the need to develop policies and procedures to govern their relationships with ethnically and culturally diverse populations: sometimes to integrate them within an imperial society and sometimes to exclude them. In some cases, these empires became victims of their own successes. By expanding their boundaries too far, they created political, cultural, and administrative difficulties that they could not manage. They also experienced environmental, social, and economic problems when they overexploited their lands and subjects and permitted excessive wealth to be concentrated in the hands of privileged classes.
I. The number and size of key states and empires grew dramatically by imposing political unity on areas where previously there had been competing states.
- Required examples of key states and empires (Student should know the location and names):
II. Empires and states developed new techniques of imperial administration based, in part, on the success of earlier political forms.
A. In order to organize their subjects, the rulers created administrative institutions including centralized governments, as well as elaborate legal systems and bureaucracies.
B. Imperial government promoted trade and projected military power over larger areas using a variety of techniques including:
- Diplomacy
- Developing Supply Lines
- Building Fortifications, Defensive Walls, & Roads
- Drawing new groups of military officers and soldiers from the locale
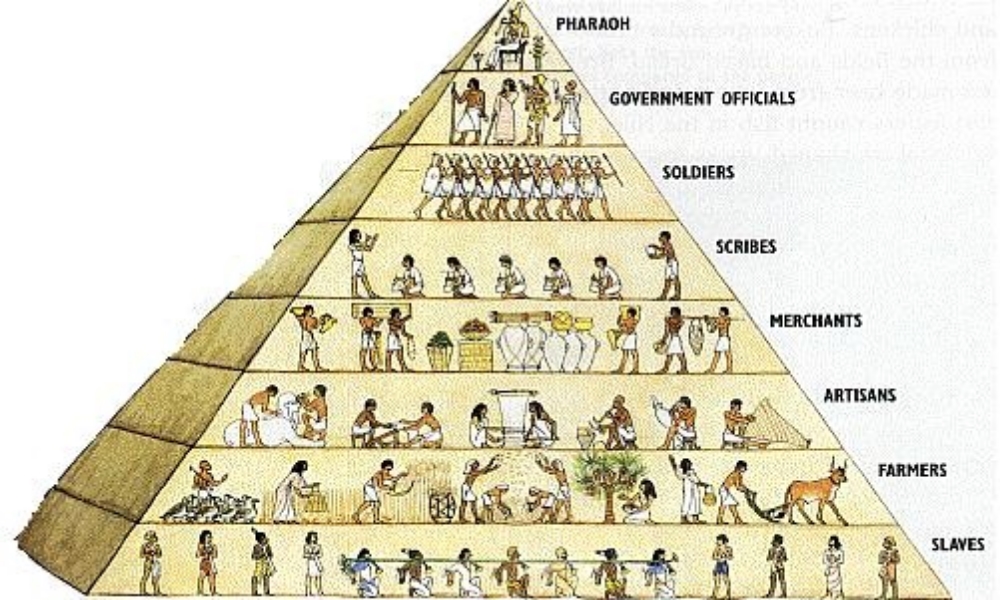
III. Unique social and economic dimensions developed in imperial societies in Afro-Eurasia and the Americas.
B. The social structures of empires displayed hierarchies that included cultivators, laborers, slaves, artisans, merchants, elites, or caste groups.
D. Patriarchy continued to shape gender and family relations in all imperial societies of this period.
IV. The Roman, Han, Persian, Mauryan, and Gupta empires created political, cultural, and administrative difficulties that they could not manage, which eventually led to their decline, collapse, and transformation into successor empires or states.
A. Through excessive mobilization of resources, erosion of established political institutions, and economic changes, imperial governments generated social tensions and created economic difficulties by concentrating too much wealth in the hands of elites.
B. Security issues along their frontiers, including the threat of invastions, challened imperial authority.
END OF AN ERA: THE DOWNFALL OF THE MAJOR CLASSICAL EMPIRES (BENN DIAGRAM)
With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically. Much of this trade resulted from the demand for raw materials and luxury goods. Land and water routes linked many regions of the Eastern Hemisphere. The exchange of people, technology, religious and cultural beliefs, food crops, domesticated animals, and disease pathogens developed alongside the trade in goods across far-flung networks of communication and exchange. In the Americas and Oceania localized networks developed.
I. Land and water routes became the basis for trans-regional trade, communication, and exchange networks in the Eastern Hemisphere.
A. Many factors, including the climate and location of the routes, the typical trade goods, and the ethnicity of people involved, shaped the distinctive features of a variety of trade routes.
II. New technologies facilitated long-distance communication and exchange.
B. Innovations in maritime technologies (Lateen Sails, Dhow Ships), as well as advanced knowledge of the monsoon winds, stimulated exchanges along maritime routes from East Africa to East Asia
III. Alongside the trade in goods, the exchange of people, technology, religious and cultural beliefs, food crops, domesticated animals, and disease pathogens developed across far-flung networks of communication and exchange.
A. The spread of crops, including rice and cotton from South Asia to the Middle East, encouraged changes in farming and irrigation techniques (The Qanat System, Noria & Sakia water wheels, and improved pumps like the Shaduf)
B. The spread of disease pathogens diminished urban populations and contributed to the decline of some empires (Effect of disease on the Roman Empire, Effect of Disease on the Chinese Empires
C. Required examples of transformed religious and cultural traditions: BUDDHISM, HINDUISM, CHRISTIANITY
The information that follows is not specifically mentioned by the College Board. However, it will make you a more culturally well-rounded person; so... you're welcome.
The Parthenon sits up on the Acropolis in the center of Athens. It is THE iconic Western work of Architecture. It served as a temple to Athena and a treasury to the Athenian Empire. There was a Parthenon before this one but the Persians destroyed it. So, they built this one instead. Later, in the 5th Century CE, they converted this temple to Athena into a temple to Mary. In the 1460s, it became an Ottoman Mosque. I always thought that it looked run down because of how old it was. Turns out, during a war between the Venetians and Ottomans, the Ottomans stored their ammo here thinking the Venetians wouldn't attack it. They were wrong.
You are looking at the oldest stone structure in India. It's a stupa. Stupas are round structures usually housing Buddhist relics. Buddhists use Stupas as places of meditation. This one was commissioned by Ashoka himself. His wife directly oversaw the construction as Sanchi was both her hometown and the site of her marrage to Ashoka.
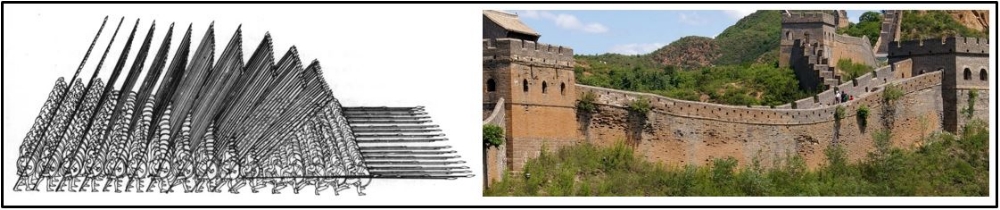
There had been walls in China for a while. They were only average walls. With their powers combined under the reign of Qin Shi Huangdi, they became the Great Wall. A theme of Chinese history that you should pick up on this year is that people from the North are constantly trying (and often succeeding) to invade China. The Wall as you know it today wasn't finished until much later (Ming Dynasty). Also, you can't see it from space. But, it's still pretty great. 13,000 miles great. It would take you 10 days to drive the length of this thing (going 60 mph with no stops...) It could replace both the US-Mexico border and the US-Canada border... twice. Sadly, around 300,000 people died in the construction of the wall.... many of which were buried within the wall!
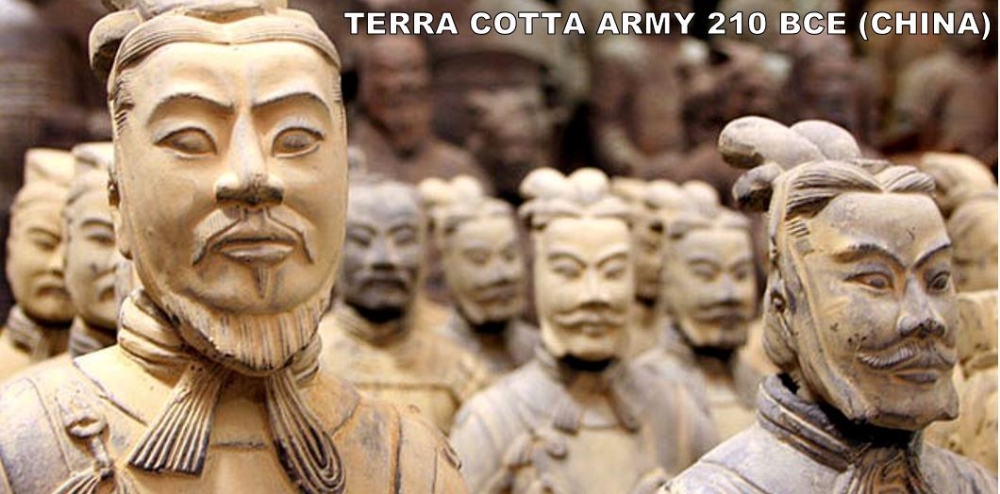
Ok. So, Qing Shi Huangdi will be the only guy to make the ART TO KNOW list twice. But, when you have the power of ALL OF CHINA behind you for the first time in history.... you can get stuff done. The Terra Cotta army is one of the most colossal wastes of time and energy ever. Qin Shi Huangdi had them constructed to defend him in the afterlife (watch me die and then be confronted by the afterlife's true ruler, Qin Shi Huangdi and his massive army). The best part of this story is that no one knew these fellas existed until 1974... Like our Lascaux Cave Paintings, these guys were discovered by accident. Some farmers were trying to dig a well. They kept finding these fragments of sculpture. These fragments were just the tip of the Terra Cotta Iceberg. I'm talking 8,000 soldiers, 130 chariots, 520 horses; most of which are still buried. They won't let you walk through the pits (they let Queen Elizabeth II, but she also got to sit on the Iron in Westeros... It's good to be the Queen).
This may surprise you, but Romans often thought they were the best thing to ever happen. They liked to mock the Ziggurats and Pyramids for serving no purpose. Enter the Aqueduct. Aqueducts carry water from fresh springs to areas without water. This one is in France. It is the highest and one of the best preserved. I'm amazed living in the Southern US and seeing Civil War battlefields. I think to myself, "Wow. This is so historic." This is about 2,000 years older. Amazing. After Rome fell, you would think that this would have been taken apart to build huts (or some other medieval junk). But, after the mineral deposits caused it to no longer carry water, it became a toll bridge. Talk about a demotion. ROMAN USE: Water to fountains, baths, homes, farms. MEDIEVAL USE: We can walk on it. This is still one of France's biggest tourist attractions.
- TAO TE CHING, 550 BCE, Lao Tzu (CHINA)
- 12 TABLES, 451 BCE (ROME)
- LESSONS FOR WOMEN, 80 CE, Ban Zhao (CHINA)
- SERMON ON THE MOUNT, 90 CE (ROME)
- CODE OF JUSTINIAN, 529 CE, Justinian (BYZANTINE)
(BESIDES ISLAM) ALL MAJOR EARTH RELIGIONS TAKE HOLD HERE.
HISTORICALLY SIGNIFICANT CIVILIZATIONS ARISE HERE (ROME, INDIA, CHINA)
MVP OF THIS ERA: THE CLASSICAL CIVILIZATIONS. HOW THEY RULE, INTERACT, and FALL.
TRADE ROUTES EMERGE AND ARE AS IMPORTANT AS RELIGION & CIVILIZATION.
THOSE RELIGIONS FROM ABOVE; GREW, SPREAD, and CHANGED FROM HERE ON.