The Post Classical Period in AP WORLD: MODERN covers from 1200-1450 CE. This is very heavy in trade and inter-connectivity. The first two of the nine units in AP WORLD: MODERN are featured in this time period. See the chart below for the exact weighting:
CLICK BELOW for pages dedicated to the TWO UNITS in this PERIOD.
Below are the ACTUAL STANDARDS provided by the College Board for what you have to know for the 1200-1450 Period:
A deepening and widening of networks of human interaction within and across regions contributed to cultural, technological, and biological diffusion within and between various societies.
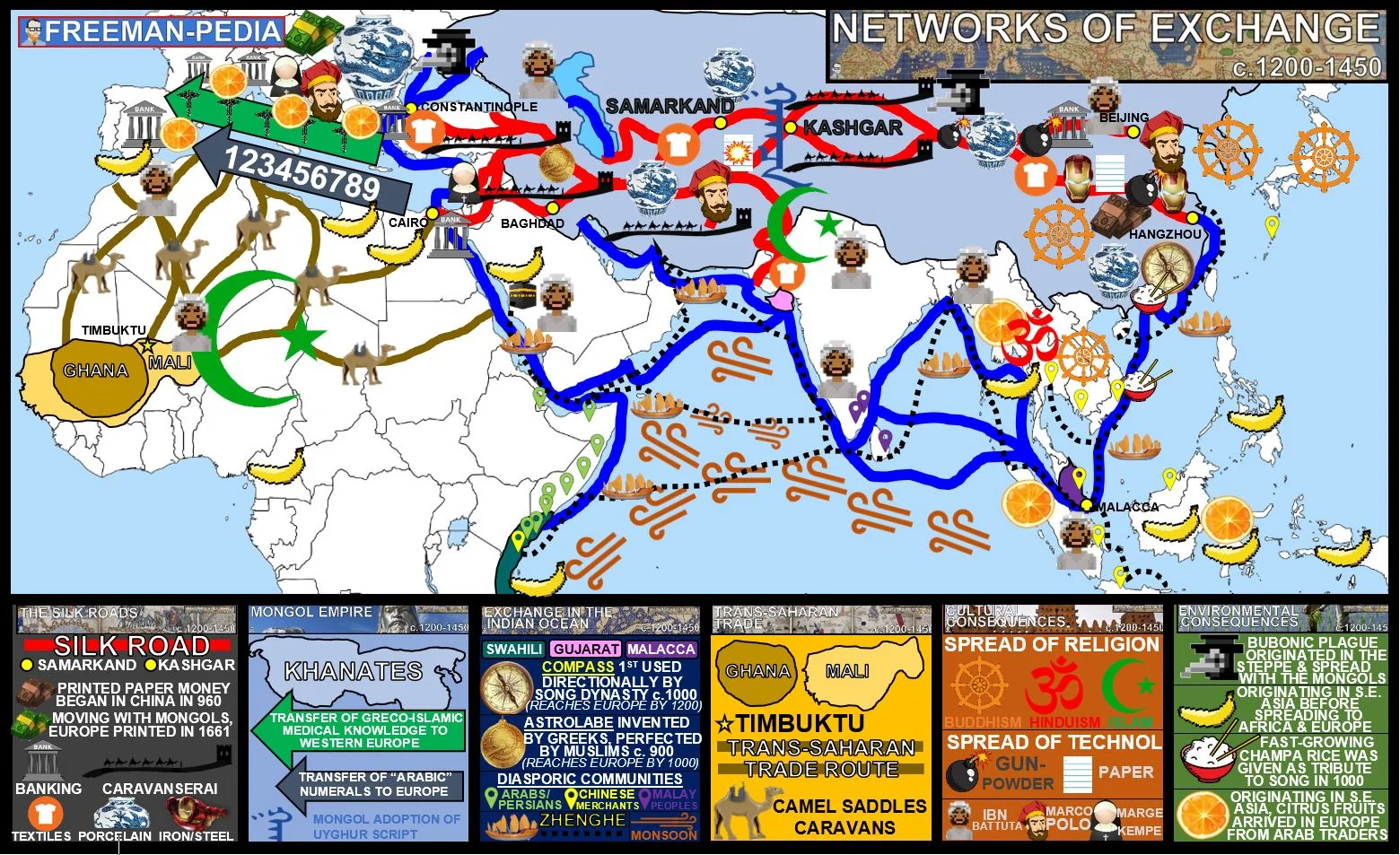
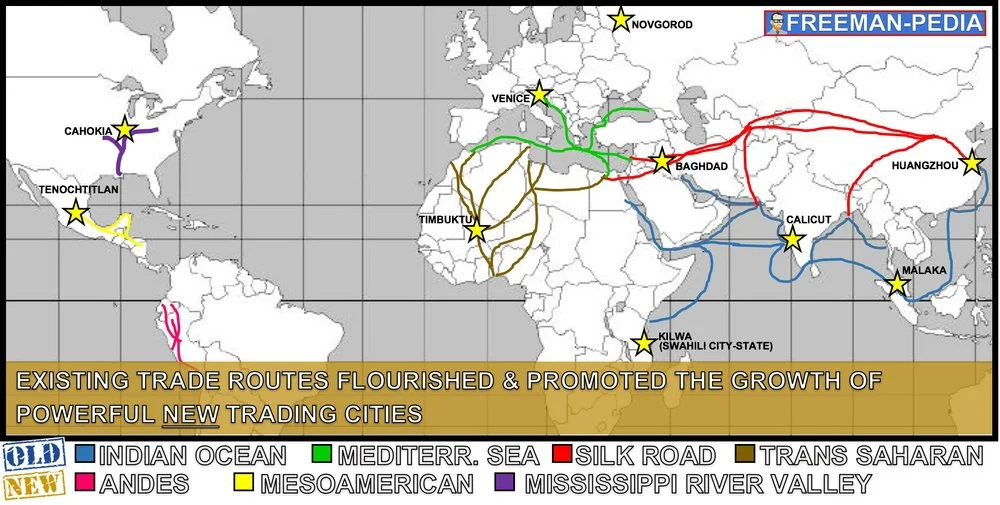
Improved commercial practices led to an increased volume of trade and expanded the geographical range of existing trade routes—including the Silk Roads, trans-Saharan trade network, and Indian Ocean—promoting the growth of powerful new trading cities.
The Indian Ocean trading network fostered the growth of states.
The growth of inter-regional trade in luxury goods (silk and cotton textiles, porcelain, spices, precious metals and gems, slaves, exotic animals)
(The Growth of Inter-regional Trade) was encouraged by innovations in previously existing transportation and commercial technologies, including the caravanserai, forms of credit, and the development of money economies as well as the use of the compass, the astrolabe and larger ship designs.
The economy of Song China flourished as a result of increased productive capacity, expanding trade networks, and innovations in agriculture and manufacturing.
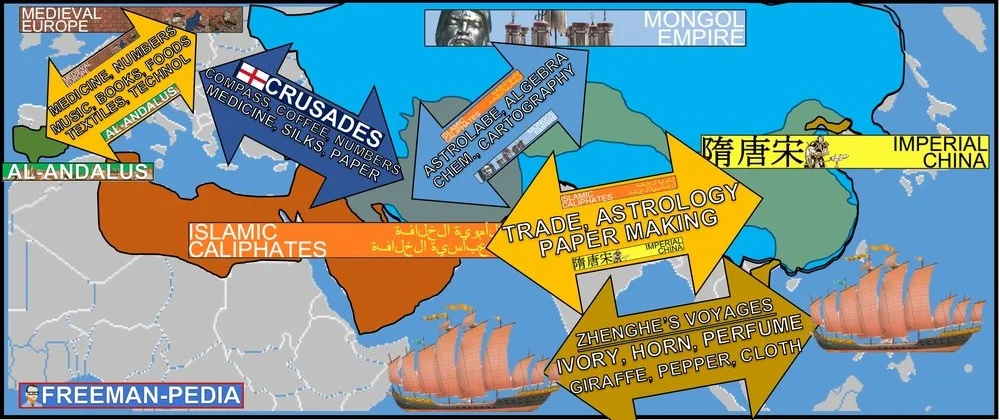
The expansion of empires—including the Mongols—facilitated Afro-Eurasian trade and communication as new people were drawn into their conquerors’ economies and trade networks.
The expansion of empires—including Mali in West Africa—facilitated Afro-Eurasian trade and communication as new people were drawn into the economies and trade networks.
The expansion and intensification of long distance trade routes often depended on environmental knowledge, including advanced knowledge of the monsoon winds. The growth of inter-regional trade was encouraged by innovations in existing transportation technologies.
Muslim rule continued to expand to many parts of Afro-Eurasia due to military expansion, and Islam subsequently expanded through the activities of merchants, missionaries, and Sufis.
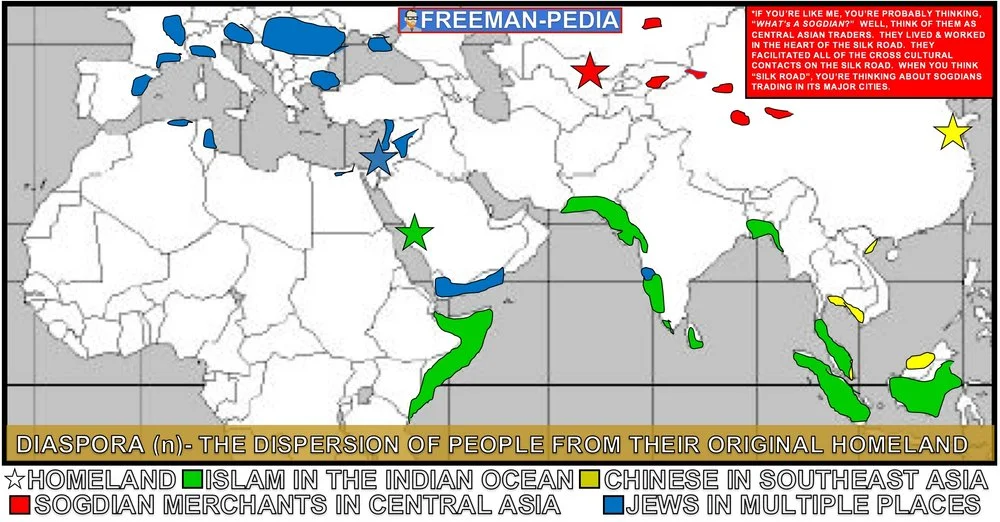
In key places along important trade routes, merchants set up diasporic communities where they introduced their own cultural traditions into the indigenous cultures and, in turn, indigenous cultures influenced merchant cultures.
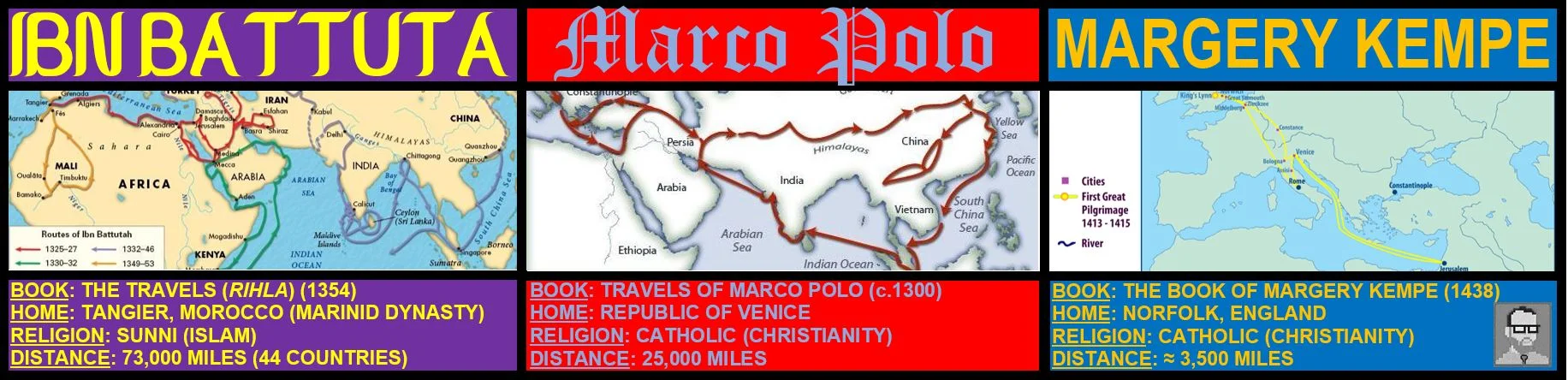
As exchange networks intensified, an increasing number of travelers within Afro–Eurasia wrote about their travels. .
Increased cross-cultural interactions resulted in the diffusion of literary, artistic, and cultural traditions, as well as scientific and technological innovation.
Chinese cultural traditions continued, and they influenced neighboring regions.
Buddhism and its core beliefs continued to shape societies in Asia and included a variety of branches, schools, and practices.
Islam, Judaism, Christianity, and the core beliefs and practices of these religions continued to shape societies in Africa and Asia.
Hinduism, Islam, and Buddhism, and their core beliefs and practices, continued to shape societies in South and Southeast Asia.
Christianity, Judaism, Islam and the core beliefs and practices of these religions continued to shape societies in Europe.
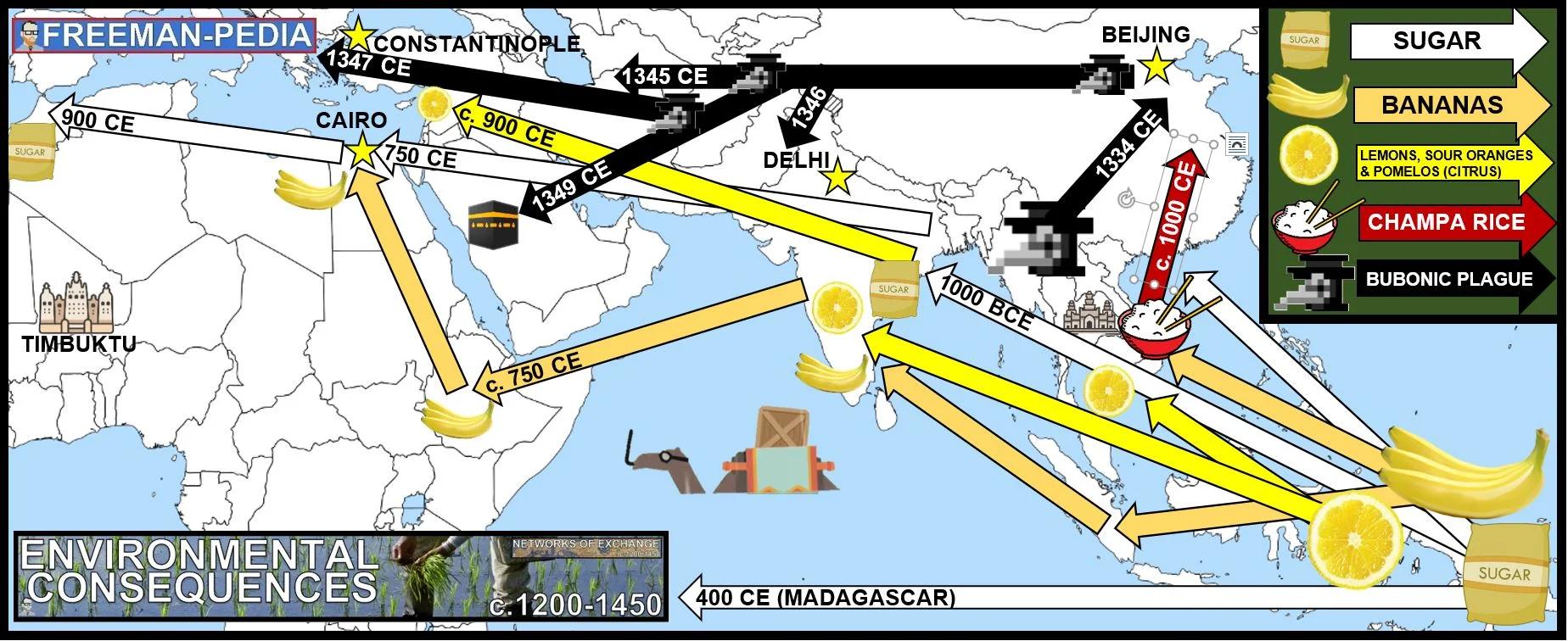
There was continued diffusion of crops and pathogens, with epidemic diseases, including the Bubonic plague, along trade routes.
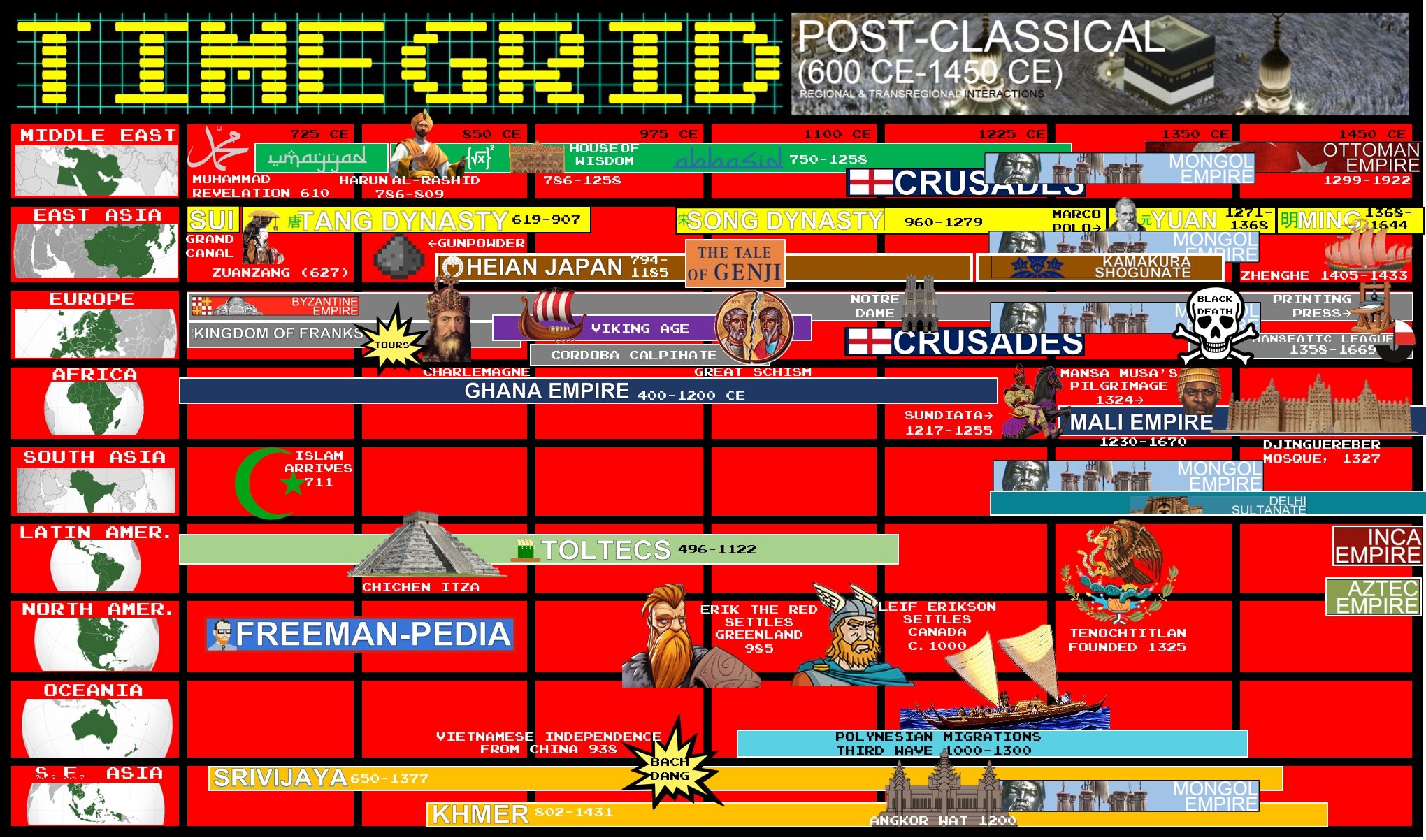
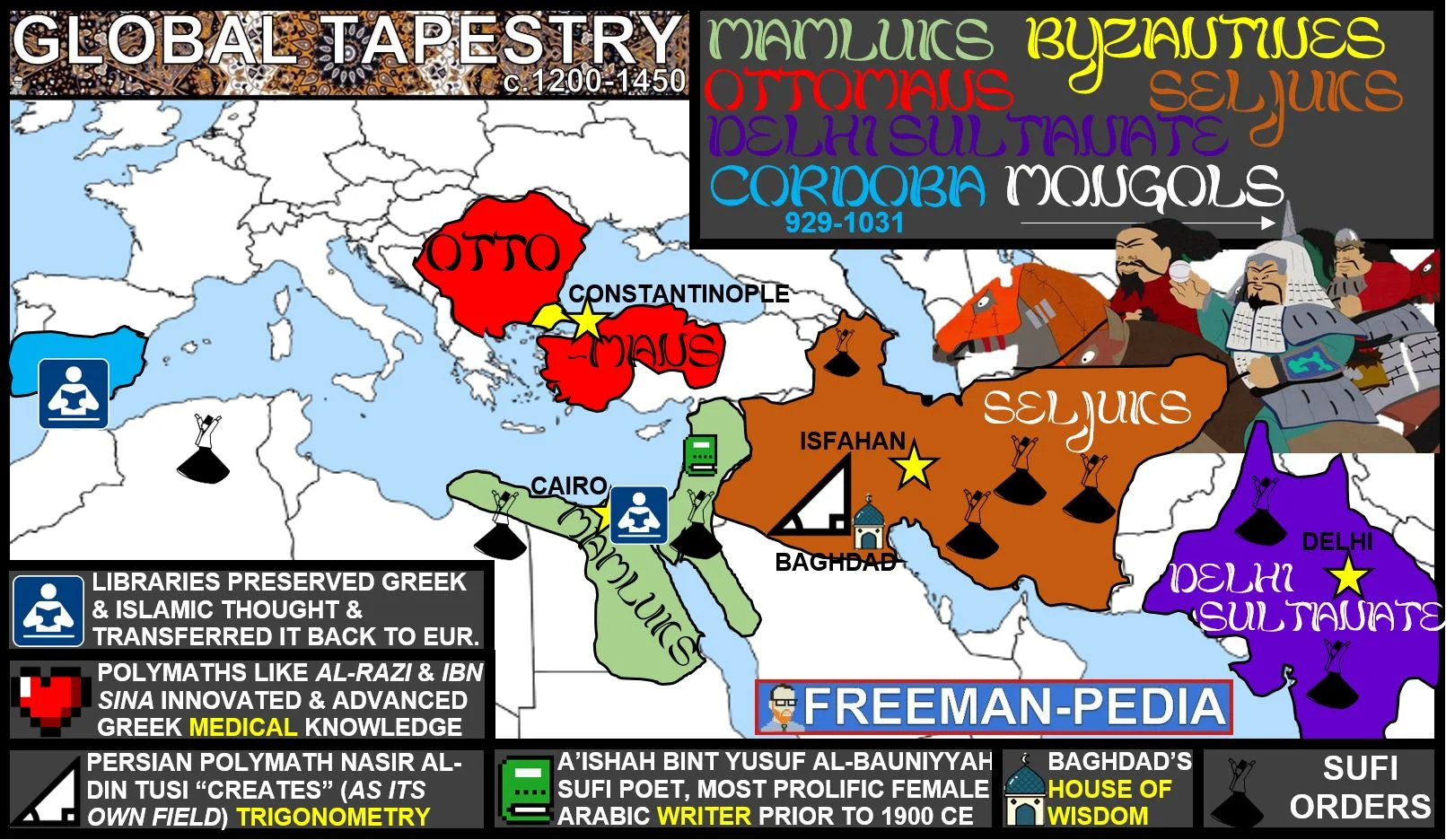
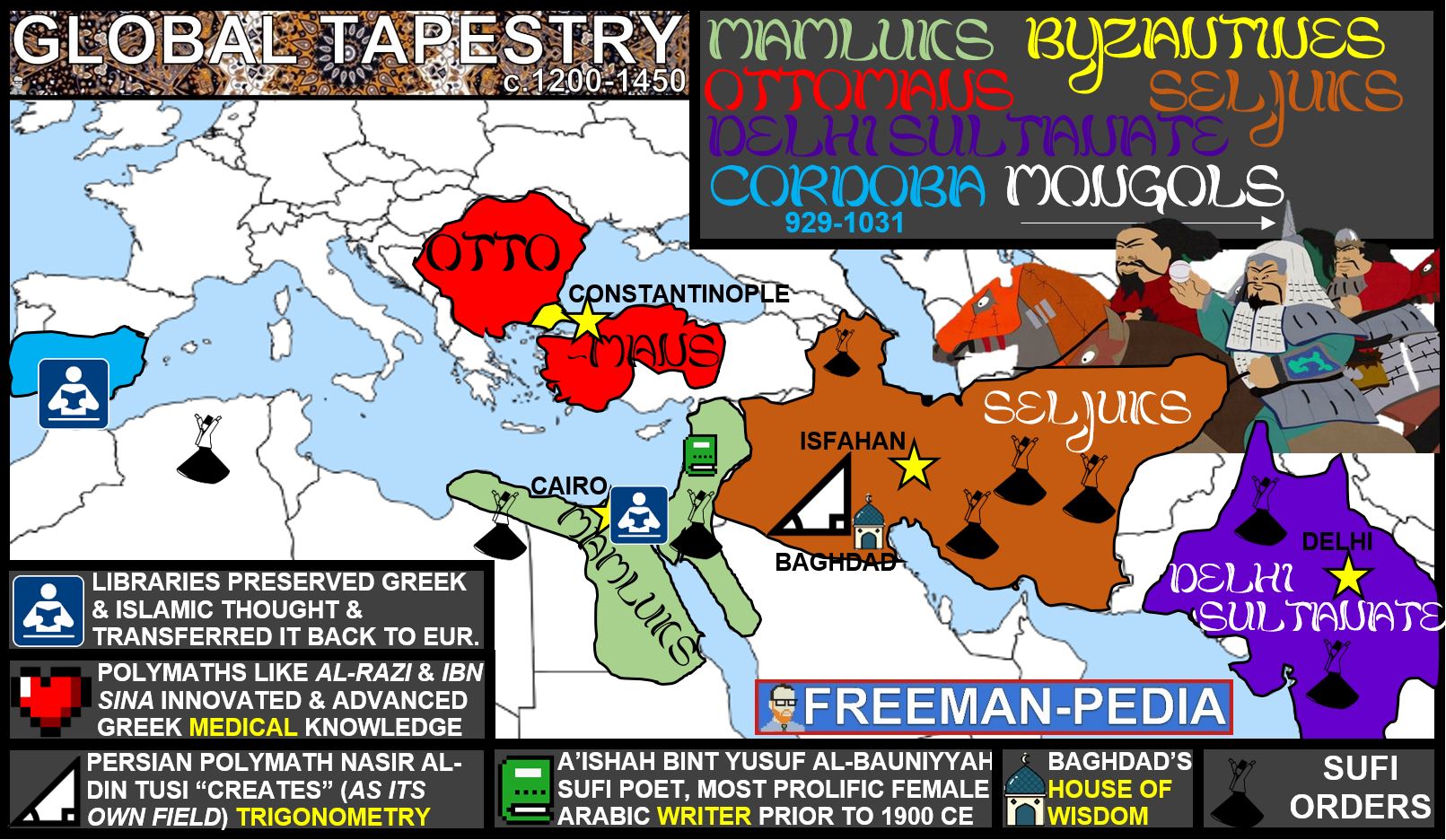
State formation and development demonstrated continuity, innovation, and diversity in various regions.
As the Abbasid Caliphate fragmented, new Islamic political entities emerged, most of which were dominated by Turkic peoples. These states demonstrated continuity, innovation, and diversity.
Empires and states in Afro-Eurasia and the Americas demonstrated continuity, innovation, and diversity in the 13th century. This included the Song Dynasty of China, which utilized traditional methods of Confucianism and an imperial bureaucracy to maintain and justify its rule.
State formation and development demonstrated continuity, innovation, and diversity, including the new Hindu and Buddhist states that emerged in South and Southeast Asia.
Europe was politically fragmented and characterized by decentralized monarchies, feudalism, and the manorial system.
Empires collapsed in different regions of the world and in some areas were replaced by new imperial states, including the Mongol khanates.
In the Americas and in Africa, as in Eurasia, state systems demonstrated continuity, innovation, and diversity, and expanded in scope and reach.
Muslim states and empires encouraged significant intellectual innovations and transfers.
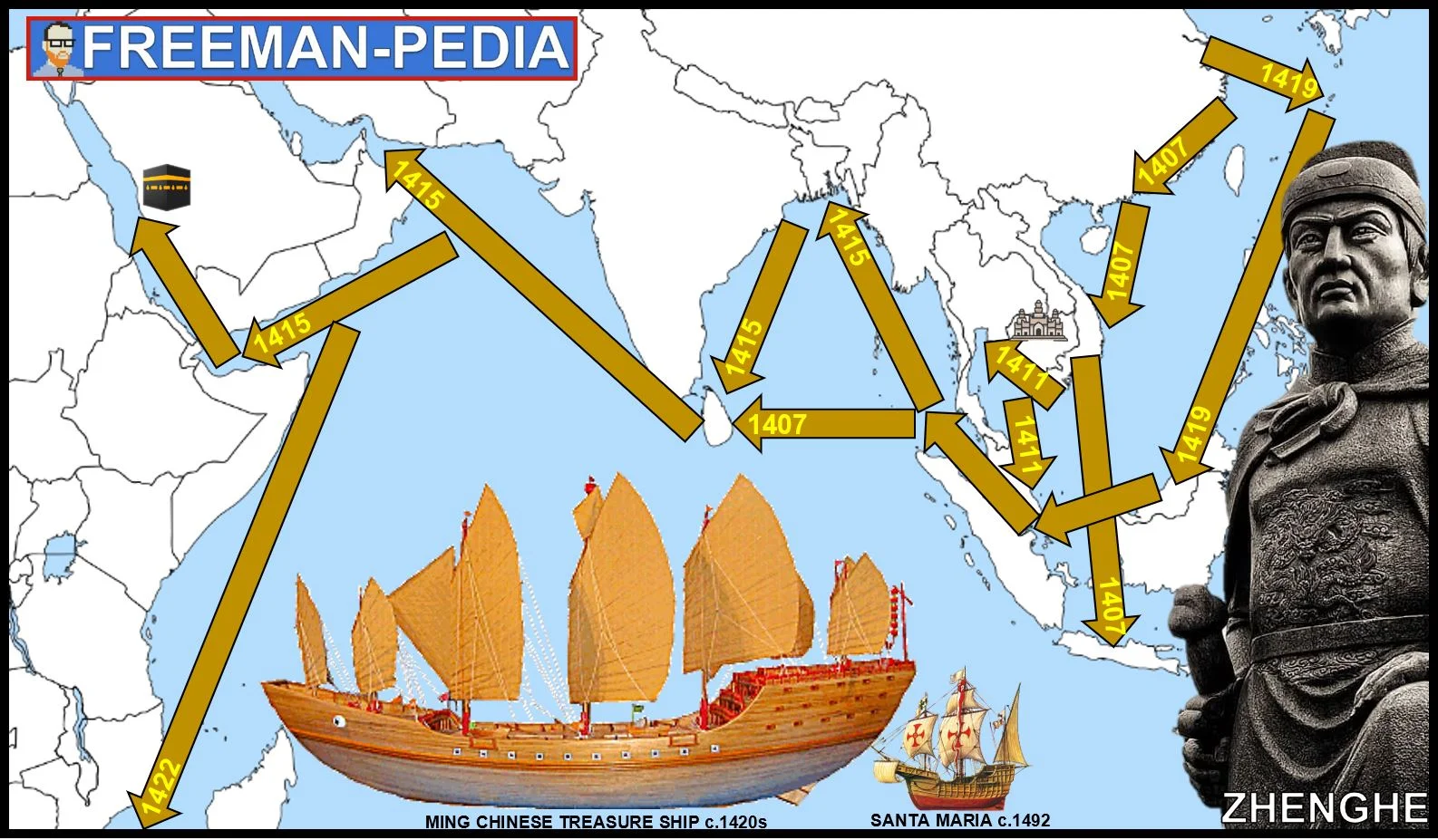
Inter-regional contacts and conflicts between states and empires, including the Mongols, encouraged significant technological and cultural transfers,
…including during Chinese maritime activity led by Ming Admiral Zheng He.
Changes in trade networks resulted from and stimulated increasing productive capacity, with important implications for social and gender structures and environmental processes.
Demand for luxury goods increased in Afro–Eurasia. Chinese, Persian, and Indian artisans and merchants expanded their production of textiles and porcelains for export; manufacture of iron and steel expanded in China.
The fate of cities varied greatly, with periods of significant decline and periods of increased urbanization buoyed by rising productivity and expanding trade networks.
The economy of Song China became increasingly commercialized while continuing to depend on free peasant and artisanal labor.
Europe was largely an agricultural society dependent on free and coerced labor, including serfdom.
For the first period of AP WORLD MODERN, the POST-CLASSICAL PERIOD (1200-1450), there are 20 people to know… and one god.