Foundations covers everything from the Big Bang up until roughly 600 BCE. Sounds like alot, right? It is. Like 13.8 billion years. Such a long time, one might think that this historical era will be the most difficult. Wrong. Don't spend too much time here. It's 5% of the test. 5%... So, don't go overboard. This era sets the stage for humanity as we know it. The main ideas are that humans evolved, left Africa, started farming, religion, invention, and social hierarchy. That's it. Move on. Things will get more specific and interesting in the following eras...
Throughout the Paleolithic era, humans developed sophisticated technologies and adapted to different geographical environments as they migrated from Africa to Eurasia, Australasia, and the Americas.
I. ARCHEOLOGICAL EVIDENCE INDICATES THAT DURING THE PALEOLITHIC ERA, HUNTER-FORAGER BANDS OF HUMANS GRADUALLY MIGRATED FROM THEIR ORIGIN IN EAST AFRICA TO EURASIA, AUSTRALIA, AND THE AMERICAS, ADAPTING THEIR TECHNOLOGY AND CULTURES TO NEW CLIMATE REGIONS.
-The term Big Geography draws attention to the global nature of world history. Throughout the Paleolithic period, humans migrated from Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas.
OUT OF AFRICA THEORY
A. Humans used fire in new ways: to aid hunting and foraging, to protect against predators, and to adapt to new/colder environments.
-Humans developed a wider range of tools specially adapted to different environments from tropics to tundra
B. People lived in small groups that structured social, economic, and political activity. These bands exchanged people, ideas, and goods.
In response to warming climates at the end of the last Ice Age, from about 10,000 years ago, some groups adapted to the environment in new ways, while others remained hunter-foragers. Settled agriculture appeared in several different parts of the world. The switch to agriculture created a more reliable, but not necessarily more diversified, food supply. Agriculturalists also had a massive impact on the environment through intensive cultivation of selected plants to the exclusion of others, through the construction of irrigation systems, and through the use of domesticated animals for food and for labor. Populations increased; family groups gave way to village life and, later, to urban life with all its complexity. Patriarchy and forced labor systems developed, giving elite men concentrated power over most of the other people in their societies. Pastoralism emerged in arts of Africa and Eurasia. Pastoral peoples domesticated animals and led their herds around grazing ranges. Like agriculturalists, pastoralists tended to be more socially stratified than hunter-foragers. Because pastoralists were mobile, they rarely accumulated large amounts of material possessions, which would have been a hindrance when they changed grazing areas. The pastoralists’ mobility allowed them to become an important conduit for technological change as they interacted with settled populations.
BEGINNING ABOUT 10,000 YEARS AGO, SOME HUMAN COMMUNITIES ADOPTED SEDENTISM AND AGRICULTURE, WHIL OTHERS PURSUED HUNTER-FORAGER OR PASTORIALIST LIFESTYLES--DIFFERENT PATHWAYS THAT HAD SIGNIFICANT SOCIAL AND DEMOGRAPHIC RAMIFICATIONS.
I. The Neolithic Revolution led to the development of more complex economic and social systems.
B. People in each region domesticated locally available plants and animals.
C. Pastoralism developed at various sites in the grasslands of Afro-Eurasia, affecting the environment in a variety of ways.
D. Agricultural communities had to work cooperatively to clear land and create the water control systems needed for crop production, drastically affecting environmental diversity.
II. Agriculture and pastoralism began to transform human societies.
A. Pastoralism and agriculture led to more reliable and abundant food supplies, which increased the population.
-Surpluses of food and other goods led to specialization of labor, including new classes of artisans and warriors, and the development of elites.
Technological innovations led to improvements in agricultural production, trade, and transportation. (Pottery, Wheels, and wheeled vehicles)
C. Patriarchal forms of social organization developed in both pastoralist and agrarian societies.
From about 5,000 years ago, urban societies developed, laying the foundations for the first civilizations. The term civilization is normally used to designate large societies with cities and powerful states. While there were many differences between civilizations, they also shared important features. They all produced agricultural surpluses that permitted significant specialization of labor. All civilizations contained cities and generated complex institutions, such as political bureaucracies, armies, and religious hierarchies. They also featured clearly stratified social hierarchies and organized long-distance trading relationships. Economic exchanges intensified within and between civilizations, as well as with nomadic pastoralists. As populations grew, competition for surplus resources, especially food, led to greater social stratification, specialization of labor, increased trade, more complex systems of government and religion, and the development of record keeping. As civilizations expanded, they had to balance their need for more resources with environmental constraints such as the danger of undermining soil fertility. Finally, the accumulation of wealth in settled communities spurred warfare between communities and/or with pastoralists; this violence drove the development of new technologies of war and urban defense.
THE APPEARANCE OF THE FIRST URBAN SOCIETIES 5,000 YEARS AGO LAID THE FOUNDATIONS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF COMPLEX CIVILIZATIONS; THESE CIVILIZATIONS SHARED SEVERAL SIGNIFICANT SOCIAL, POLITICAL, AND ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS.
1. Core and foundational civilizations developed in a variety of geographical and environmental settings where agriculture flourished.
II. The first states emerged within core civilizations in Mesopotamis and the Nile River Valley.
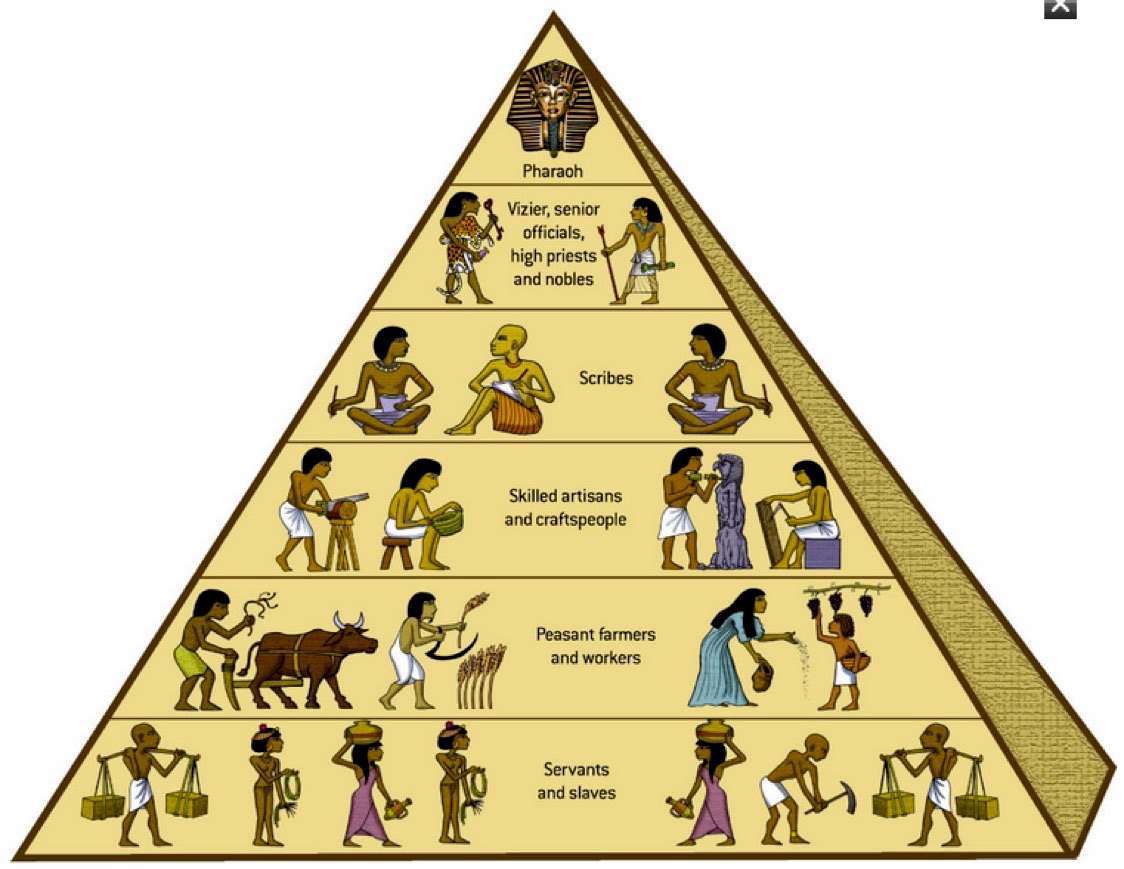
A. States were powerful new systems of rule that mobilized surplus labor and resources over large areas. Rulers of early states were often claimed divine connections to power. Rulers also relied on the support of the military, religious, or aristocratic elites.
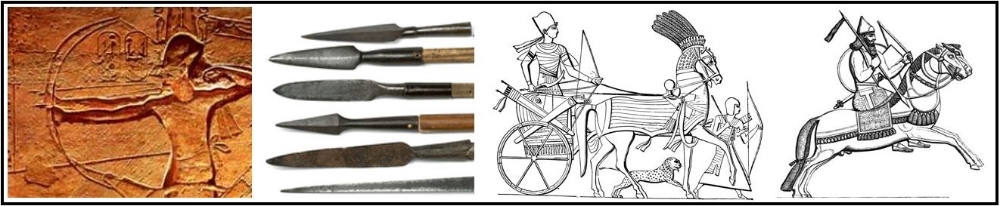
B. As states grew and competed for land and resources, the more favorably situated — including the Hittites who had access to IRON— had greater access to resources, produced more surplus food, and experienced growing populations, enabling them to undertake territorial expansion and conquer surrounding states. .
C. Pastoralists were often the developers and disseminators of new weapons (Compound Bows, Iron Weapons) and modes of transportation (Chariots, Horseback riding) that transformed warfare in agrarian civilizations.
III. Culture played a significant role in unifying states through laws, language, literature, religion, myths, and monumental art.
B. Systems of record keeping arose independently in all early civilizations and writing and record keeping subsequently spread. (Cuneiform, Hieroglyphs)
C. States developed legal codes that reflected existing hierarchies and facilitated the rule of governments over people (Code of Hammurabi in Babylonia, Code of Ur-Nammu in Sumer)
D. New religious beliefs developed in this period-- (Vedic Religion, Hebrew Monotheism, Zoroastrianism)-- continued to have strong influences in later periods.
F. Social hierarchies, including patriarchy, intensified as states expanded and cities multiplied.
The information that follows is not specifically mentioned by the College Board. However, it will make you a more culturally well-rounded person; so... you're welcome.
Found in 1940 by 18-year-old Marcel Ravidat by accident, these 2,000 figures were painted on the walls 17,300 years ago. Most of the images are animals and most of those are horses. Fossil evidence from the time show that these animals actally existed in this region at this time. It is easily the most well known Paleolithic Art of all time.
Look at these things... The last of the Great Wonders of the World to still exist, the Pyramids of Egypt may be the most iconic architecture on earth. That big one in the middle (Khufu) is not only the oldest of the big three, but it was also the tallest man made structure on earth for 3,800 years (until several European Cathedrals surpassed it). Pyramids were used as tombs for Egyptian Pharaohs and are the most recognizable monolithic architecture in the world.
Ziggurats are awesome. This is what's left of the Ziggurat of Ur. It's just the base, so people have speculated that there was more here. It was built by the Sumerians for their moon god (which was the patron god of Ur).
Oracle Bones were used in Shang China (and probably before) to communicate with the gods (aka Divination). They would ask the gods a question and then heat the Oracle bones until they cracked. They would then analyze the cracks for messages from the gods. More importantly, these bones show that China had writing. Many of these bones were buried in pits like this one. The picture in the bottom right is a turtle shell.
This head is about as tall as you are. There are at least 17 of these bad boys along the coast of Meso-America along the Gulf of Mexico. They all kinda have this look on their face. Each head has a distinctive headdress leading us to believe that each one is a distinct Olmec ruler. My favorite part? They're all slightly cross-eyed!
- HAMMURABI's CODE, 1700 BCE (BABYLON)
- EPIC OF GILGAMESH, 1700 BCE (BABYLON)
- RIG VEDA, 1700 BCE (INDIA)
- BOOK OF THE DEAD, 1500 BCE (EGYPT)
- BOOK OF SONGS, 1000 BCE (CHINA)
HUMANS LEFT AFRICA AND BEGAN USING TOOLS & FIRE.
NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION (FARMING) AROUND THE RIVER VALLEYS GAVE WAY TO CIVILIZATION.
CIVILIZATION BROUGHT STRATIFICATION & SPECIALIZATION,
CIVILIZATION BROUGHT MASSIVE ARCHITECTURE AND WRITING.
TWO EARLY RELIGIONS BEGIN IN THIS ERA (HINDUISM/JUDAISM)